Analyzing gender inequality through large-scale Facebook advertising data
Abstract
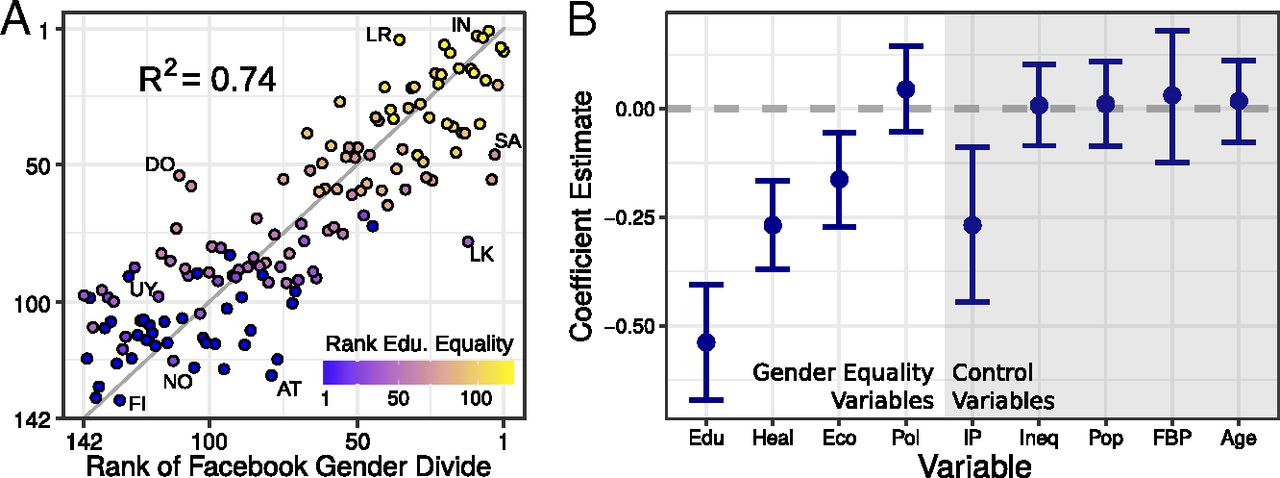
Significance We present the Facebook Gender Divide, an inexpensive, real-time instrument for measuring gender differences in Facebook access and activity in 217 countries. The Facebook Gender Divide captures standard indicators of Internet penetration and gender equality indices in education, health, and economic opportunity. We find that the tendency of countries to approach economic gender equality is negatively associated with a high Facebook Gender Divide. Our results suggest that online social networks, while suffering gender imbalance, may lower information access barriers for women and narrow the economic gender gap. , Online social media are information resources that can have a transformative power in society. While the Web was envisioned as an equalizing force that allows everyone to access information, the digital divide prevents large amounts of people from being present online. Online social media, in particular, are prone to gender inequality, an important issue given the link between social media use and employment. Understanding gender inequality in social media is a challenging task due to the necessity of data sources that can provide large-scale measurements across multiple countries. Here, we show how the Facebook Gender Divide (FGD), a metric based on aggregated statistics of more than 1.4 billion users in 217 countries, explains various aspects of worldwide gender inequality. Our analysis shows that the FGD encodes gender equality indices in education, health, and economic opportunity. We find gender differences in network externalities that suggest that using social media has an added value for women. Furthermore, we find that low values of the FGD are associated with increases in economic gender equality. Our results suggest that online social networks, while suffering evident gender imbalance, may lower the barriers that women have to access to informational resources and help to narrow the economic gender gap.
Citation
Analyzing gender inequality through large-scale Facebook advertising dataGarcia, David and Mitike Kassa, Yonas and Cuevas, Angel and Cebrian, Manuel and Moro, Esteban and Rahwan, Iyad and Cuevas, Ruben
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2018) [Full Text]